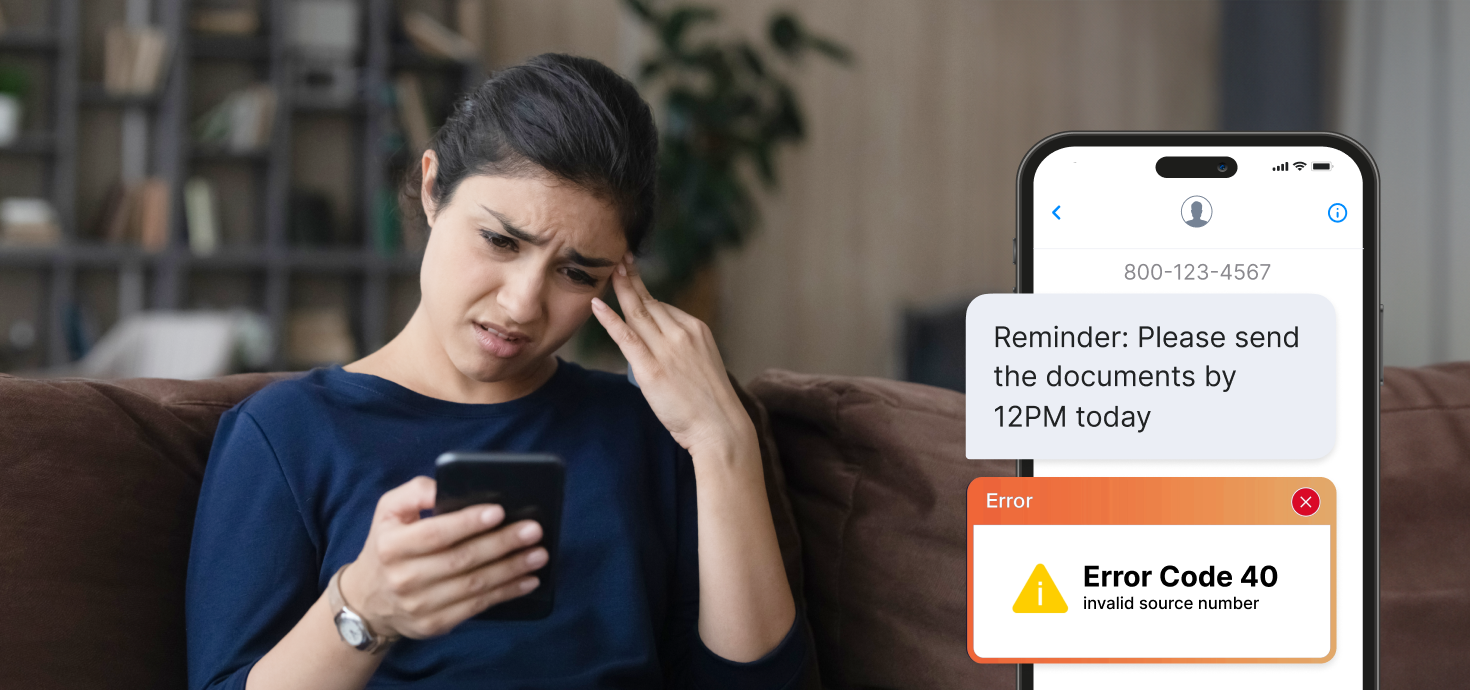
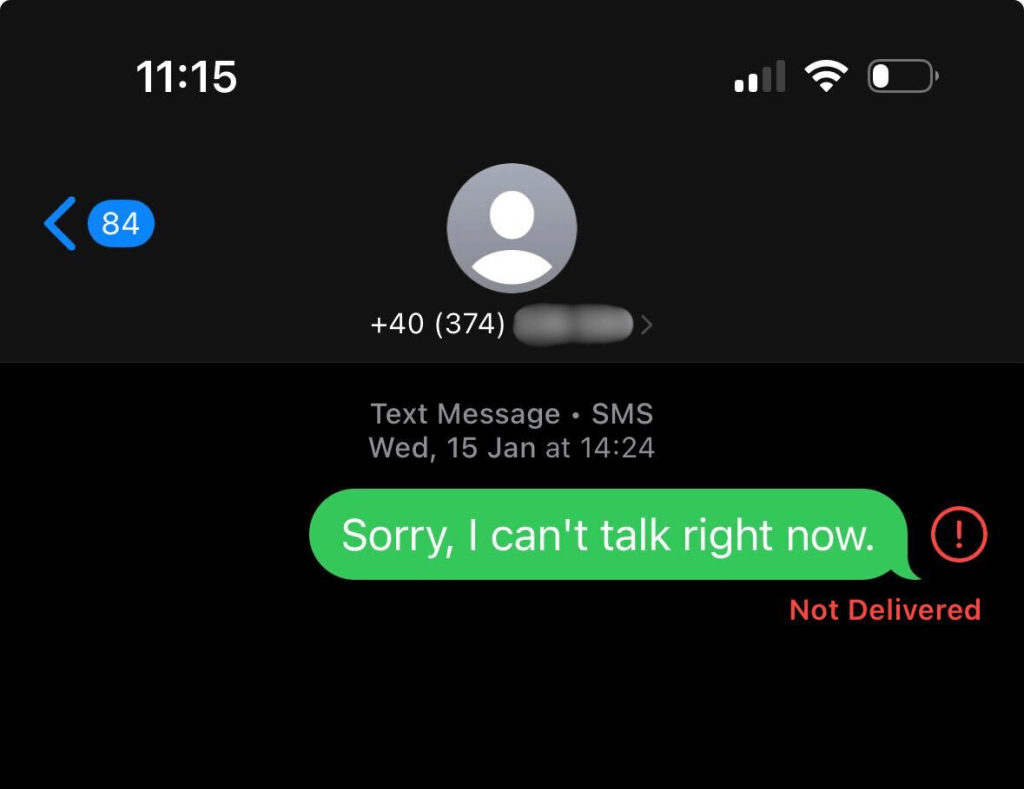
You know that moment when you hit “send” and… nothing happens? Your message simply won’t go through. It’s frustrating, especially when you’re running a campaign, chasing a lead, or sending a last-minute update.
SMS is one of the most effective communication tools available today. It’s fast, personal, and has sky-high open rates. But that doesn’t mean it’s flawless.
Even the most reliable messaging systems run into problems. Messages get delayed, dropped, or blocked, sometimes without warning.
In this guide, we’ll break down:
- What common SMS error codes mean
- Why your texts aren’t being delivered
- How to fix delivery issues
- How to spot fake error messages
What are text message errors?
A text message error is any issue that prevents your message from being successfully delivered to the recipient. Most modern messaging platforms will notify you when this happens, usually with a status like Failed, Not Delivered, or Rejected.
Behind these statuses are error codes – short numeric indicators that tell you why the message didn’t go through. These codes help identify whether the problem was caused by a network outage, a bad number, spam filtering, or something else. These error codes are important for diagnosing the underlying problem.
While error codes vary slightly between SMS providers, many are standardized and fall into clear categories like:
- Delivery issues
- Invalid numbers
- Carrier blocks
- Compliance issues
- Technical errors
How to tell if a message wasn’t delivered
Not every message that goes quiet is ignored, some never make it to the recipient in the first place. Here’s how to recognize the difference:
SMS delivery reports
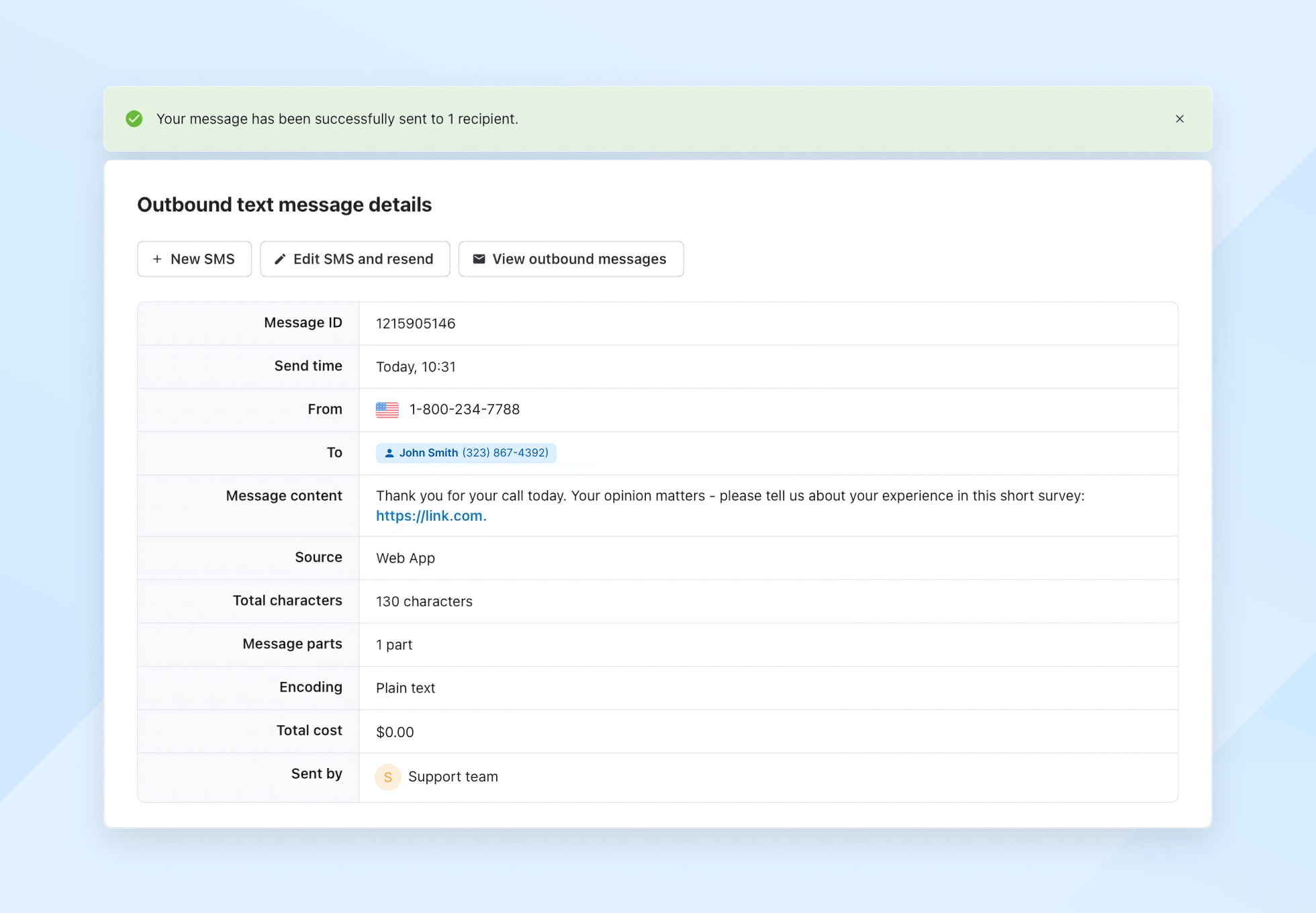
When sending messages with Textmagic, you can track delivery in real time via the Outbound SMS section. You’ll see clear status labels like:
- Delivered: The message was successfully received by the recipient’s device.
- Sent: The message left your system and is on its way, but delivery is not yet confirmed.
- Queued: The message is waiting to be sent, typically due to high traffic or carrier load.
- Failed / Not Delivered / Rejected: The message didn’t go through due to an error. You’ll usually see a related error code.
These statuses give you a live view of what’s happening and what might be going wrong.
When no response might mean no delivery
Sometimes, delivery issues hide behind what looks like poor engagement. For example:
- You send a campaign and get zero replies across the board
- Multiple messages show “Failed” or “Not Delivered” in your reports
- You’re messaging from a new or unverified number (especially in the U.S. or regions with strict filtering)
In these cases, the problem might not be the message content, it could be delivery failure.
7 Common types of text message errors
The following text message error codes typically represent generic issues that can occur in SMS messaging processes. These codes are generally standardized across different SMS gateways and APIs to a certain extent, ensuring a common understanding of basic SMS issues across platforms.
While the basic types of text message errors are standardized (invalid destination, spam detected, etc.), the exact definitions, numerical designations, and responses to these errors can vary by provider.
Each SMS provider might:
- Choose to define error conditions slightly differently based on their infrastructure or interpretation.
- Offer different levels of detail in their error reporting.
- Provide different mechanisms for handling or resolving these errors.
It’s important to understand that not all text messages sent will successfully reach their intended recipients. In cases where a message fails to deliver, you will receive a delivery report detailing the reason for the failure.
Similar to instances of delayed messages, there are various factors that can cause a message to fail. Each cause is associated with a specific error code. Here are some of the most common text message error codes and what they typically indicate, categorized by type:
Delivery errors
| Code | Error | What this means |
|---|---|---|
| 006 or 61 | Message Expired | The message was not delivered within the allowed time frame, often due to the recipient’s phone being off or out of service area for too long. |
| 20 | Network Error | There was a failure in the network, preventing the message from being delivered. This could be due to congestion or a disruption in service. |
| 80 | Destination Temporarily Unavailable | The recipient’s device may be temporarily unreachable, such as being switched off or out of coverage area. |
Validation errors
| Code | Error | What this means |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | Invalid Message | The content of the SMS does not meet the format or content requirements, possibly due to unsupported characters or incorrect encoding. |
| 40 | Invalid Source Number | The sender’s number is incorrect, not recognized, or not allowed to send messages. |
| 50 | Invalid Destination Number | The recipient’s number is incorrect, inactive, or blocked, preventing delivery. |
Permanent barriers
| Code | Error | What this means |
|---|---|---|
| 70 | Destination Permanently Unavailable | The destination number has been permanently deactivated or is no longer in service. |
Technical errors
| Code | Error | What this means |
|---|---|---|
| 300 | Invalid Destination | The destination number is blocked or deactivated. |
| 301 | Network Timeout | The message didn’t reach the carrier due to a timeout. |
| 302 | Routing Error | The message could not be routed to the specified number. |
Format errors
| Code | Error | What this means |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | Invalid Number Format | The phone number is formatted incorrectly. |
| 401 | Encoding Error | The SMS contains characters that are not supported by the network or recipient’s device. |
| 402 | Empty Message | The SMS does not contain any text. |
Compliance & spam errors
| Code | Error | What this means |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | Spam Detected | The message was flagged as spam by the network or recipient’s carrier, possibly due to the nature of the content or frequency of sending. |
| 500 | Unauthorized Sender ID | The sender ID used is not approved for use in the destination country or network. |
| 501 | Spam Detected | The message content violates anti-spam regulations. |
| 502 | Opt-Out Violation | Sending SMS to a number that has opted out of receiving messages. |
Carrier errors
| Code | Error | What this means |
|---|---|---|
| 600 | Carrier Rejection | The carrier has blocked the message based on content or sender policies. |
| 601 | Content Blocked | Specific message content has been flagged and blocked by the carrier. |
| 602 | Carrier Network Issue | An issue on the carrier’s network prevented message delivery. |
These text message error codes provide specific feedback regarding the nature of the issue encountered during the SMS transmission process. This helps diagnose issues effectively.
Please keep in mind that for precise definitions and additional codes, you should refer to the documentation provided by your specific SMS gateway or service provider.
Why your text messages aren’t getting through
Even if your SMS system is technically working, a wide range of issues, from network hiccups to compliance violations, can prevent your messages from being delivered. Let’s look at the most common causes and what you can do about them:
1. Poor or no network coverage
If your recipient’s phone is turned off, in airplane mode, or in a no-signal zone, your message won’t get through. Most carriers will retry for a short period, but eventually, the message will expire (usually with error code 006 or 61).
The problem could also lie with your hosting account. If it’s overloaded, it will struggle to send the required messages. Hosts try to avoid this by implementing various technological solutions. For example, ScalaHosting offers most of its plans with LiteSpeed Web Server, which is supposed to make the service much more reliable under heavy load.
Solution: Check for delivery patterns in a specific region or carrier. If you’re seeing clustered failures, contact your SMS provider to rule out larger outages.
2. Invalid or outdated phone numbers
Deactivated numbers, typos, landlines entered as mobile numbers – all of these reduce deliverability and waste your messaging budget.
Solution: Use Textmagic’s Carrier Lookup or services like NumVerify to validate numbers in bulk before sending. Set up automated revalidation every 3–6 months to keep your list clean and healthy.
3. Sending to purchased or unverified lists
That “qualified list” you bought? It’s likely full of cold numbers, bots, or worse – potential legal issues. In many regions, sending unsolicited texts without opt-in breaks laws like TCPA, GDPR, or PECR.
Risks include:
- Messages getting flagged as spam
- Blacklisting or fines
- Damaged sender reputation
Solution: Build your list organically with proper opt-ins. It’s slower, but much safer and far more effective than buying lists from unverified sources.
4. Geographic & carrier restrictions
Each country has unique SMS rules like 10DLC in the U.S., GDPR in Europe, or sender ID restrictions in India. If you’re not compliant, messages can be silently filtered or rejected.
Solutions:
- Use a platform like Textmagic, which supports 10DLC texting and toll-free number (TFN) verification
- Automate consent capture and campaign registration
- Use sender IDs approved for each target region
5. Device-level issues
Older devices (especially prepaid models) may have limited SMS storage. If their inbox is full, your message won’t be delivered. Also, powered-off phones or those with a dead battery will remain unreachable.
Solution: If you consistently see “Delivered” status but get no replies, check if the issue is device-related, especially for repeat recipients.
6. The recipient blocked you or opted out
If someone replies with STOP, UNSUBSCRIBE, or QUIT, you’re legally required to stop messaging them. If you keep sending, your messages may be filtered or flagged by carriers.
Solutions:
- Use a clear opt-out footer (e.g., “Reply STOP to unsubscribe”)
- Maintain a real-time suppression list
- Use double opt-in to reduce mistaken subscriptions
7. Spammy language and repetitive patterns
Carriers use advanced filters to detect SMS spam. Red flags include:
- ALL CAPS, too many !!!, or “too good to be true” phrases
- Overused words like “Free”, “Buy Now”, “Limited Time”
- Repetitive, identical messages sent to large lists
Solution: Personalize your messages, vary content using A/B tests, and write like a human. Message diversity reduces spam risk.
8. Suspicious or shortened links
Using link shorteners like bit.ly or tinyurl? Carriers often flag them as risky since they obscure the destination.
Solution:
- Use branded short links (e.g., yourbrand.com/deal)
- Limit to one link per message
- Avoid “Click here” phrasing without context
How to stay safe from fake text message errors
Identifying a fake error text message, especially in the context of phishing or scam attempts, is essential when it comes to protecting your personal information and computer system.
Here’s a quick guide on how to spot a fake error text message and what to look for:
Check the source
- Legitimate origin: If an error text message from a suspicious sender includes links for more information, it could be a scam. Always make sure links are legitimate before clicking, especially if they claim to be from your provider.
Analyze the content
- Spelling and grammar: Legitimate messages will rarely have spelling or grammatical errors. Fake messages often contain such mistakes.
- Urgency and threats: A fake error message text may create a sense of urgency or threaten dire consequences if not addressed immediately, such as data loss or legal action.
Review the instructions
- CTA: Be suspicious of text message errors that instruct you to download software, click on a link, or provide personal information.
- Contact information: Legitimate error message texts rarely provide phone numbers. Scammers often include a support number to trick you into contacting them.
Use mobile security software
- Scanning: Use reputable mobile antivirus and anti-malware software to scan your system if you suspect that the error text message might be part of a phishing attempt or malware attack.
Check the error online
- Search the error: Look up the error message text online to see if other users have reported similar issues or if the manufacturer has noted it as a known issue or scam.
Seek professional advice
- IT support: If you’re unsure whether an error text message is legitimate, contact your IT department (if you received the text on your work number) or a professional tech support service for advice.
Conclusion
Text messaging remains one of the most powerful tools in business communication, but only if your messages are actually delivered.
By understanding how SMS delivery works, why it fails, and how to fix common issues, you’re not just avoiding headaches, you’re protecting engagement, trust, and performance.
✅ Clean your lists regularly
✅ Use verified numbers and sender IDs
✅ Avoid spammy phrasing and shady links
✅ Stay compliant with opt-in best practices
✅ Monitor delivery reports and ask for help when needed
Whether it involves adjusting message content, verifying phone numbers, or contacting your service provider for specific text message errors, taking proactive steps to troubleshoot and fix text message errors will help maintain seamless communication flows.
Ultimately, staying informed about potential SMS pitfalls and knowing how to handle them effectively is essential for both businesses and individuals relying on this communication tool.
Validate contact lists
Use Textmagic’s Carrier Lookup to validate numbers and ensure every message gets through.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Your texts may not be sending or getting delivered due to issues like poor network coverage, invalid numbers, carrier filtering, or the recipient opting out. Messages sent from unregistered or unverified numbers – especially in regions with strict rules like the U.S. -may be blocked.
To improve deliverability, use verified 10DLC or toll-free numbers (TFNs), maintain a clean contact list, and avoid spammy content.
Yes, carriers may block messages that contain suspicious or spammy language (like “FREE” or “WIN”) or use public short links (e.g., bit.ly). To avoid this, use branded links, limit promotional language, and personalize your content.
“Sent” means the message was handed off to the carrier, but delivery isn’t confirmed. “Delivered” means the recipient’s device successfully received the message. If messages stay in “Sent” without moving to “Delivered”, it may indicate filtering, blocking, or network issues.
You can find SMS error codes in your messaging platform’s delivery reports.
In Textmagic, these are located in the Outbound SMS section, where each message includes a status and, if failed, an associated error code. These codes help identify the exact reason for delivery failure so you can troubleshoot effectively.
Invalid numbers often lead to immediate delivery failures. To avoid wasting messages, use a carrier lookup tool to validate your contact list before sending. This helps detect deactivated numbers, landlines, and format errors.
Related articles
What is cloud telephony and how does it work?
The evolution of business communication has been mar...
How to create a loyalty program customers will love
Fostering customer loyalty nowadays involves more th...
Mobile live chat and real-time customer service
Playing guinea pig for your company’s new software r...
Texting in the UK: How to create a compliant SMS campaign
Text message marketing is completely legal in the UK...
Mastering customer advocacy: 5 Strategies for business growth
Read our latest guide to find out how you can improv...